Financial planning is managing your money and ensuring a secure financial future. Individuals can set objectives, control spending, save and invest money intelligently, manage risks, and assure their own and their family’ financial security by developing a thorough financial plan. In this post, we’ll look at the value of financial planning, its essential elements, how to put one together, typical mistakes to avoid, the function of financial advisors, financial planning at various phases of life, practical tools and resources, and more.

- Introduction to Financial Planning :
- Fundamentals of financial planning
- Key Components of Financial Planning / Types of Financial Planning / 6 areas of financial planning
- Steps to Create a Financial Plan
- Tips for Successful Financial Planning / How to Make a Financial Plan.
- Common Financial Planning Mistakes to Avoid
- The Role of Financial Advisors
- Why it is important to plan one's own finances?
- How Much Money required for Financial Planning?
- What are the 5 steps of financial planning?
- What are the 4 basics of financial planning?
- Financial planning case study examples
- Financial planning for business owners
- Financial planning questionnaire
- Conclusion
- FAQs :
Introduction to Financial Planning :
What is Financial Planning ? Definition of financial planning.
The practise of managing and organising one’s finances in order to attain financial goals and ensure a secure financial future is known as financial planning. It entails assessing one’s existing financial status, establishing specific goals, and developing a plan of action to reach those goals. Budgeting, saving, investing, risk management, tax preparation, and estate planning are just a few of the many facets of financial planning. It seeks to maximise income, regulate spending, increase wealth, guard against financial dangers, reduce tax obligations, and facilitate the orderly transfer of assets. Individuals can take charge of their financial health and work towards a prosperous future by engaging in smart financial planning.
Importance of financial planning.
Financial planning is a methodical process for achieving one’s objectives in life. A financial plan serves as a roadmap for your financial future. In essence, it assists you in maintaining control over your sources of income, costs, and assets so that you may manage your finances and accomplish your goals.
Benefits of effective financial planning
Effective financial planning offers numerous benefits that can significantly improve your financial well-being and overall quality of life. Here are some key benefits of effective financial planning:
- Goal achievement: Financial planning helps you set realistic and achievable financial goals, such as buying a home, funding education, or planning for retirement. By creating a roadmap to reach these goals, you can allocate resources effectively and make informed decisions to ensure success.
- Improved cash flow management: By developing a budget and tracking your income and expenses, effective financial planning enables you to identify areas for cost reduction and optimize your cash flow. This ensures that you can meet your financial obligations and avoid unnecessary debt.
- Increased savings and investments: Financial planning encourages disciplined saving and investing habits, helping you grow your wealth over time. By selecting appropriate investment vehicles based on your risk tolerance and financial goals, you can maximize your returns and achieve long-term financial stability.
- Reduced debt burden: Effective financial planning includes strategies for managing and reducing debt. By prioritizing debt repayment and minimizing interest payments, you can improve your credit score and free up resources for other financial goals.
- Tax optimization: Financial planning helps you take advantage of available tax deductions, credits, and tax-advantaged investment vehicles, minimizing your tax liability and maximizing your after-tax income.
- Secure retirement: A well-executed financial plan ensures that you have sufficient savings and investments to maintain your desired lifestyle during retirement. This provides financial security and peace of mind as you transition into your golden years.
- Risk management: Effective financial planning involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. This includes obtaining appropriate insurance coverage and diversifying your investment portfolio to protect your financial well-being in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
- Enhanced financial independence: By achieving your financial goals and growing your wealth, effective financial planning can help you attain financial independence. This allows you to maintain your desired lifestyle without relying on a regular paycheck, providing greater flexibility and freedom.
- Efficient estate planning: Financial planning ensures the efficient transfer of your assets to your beneficiaries, minimizing potential tax liabilities and legal complications. This includes drafting a will, setting up trusts, and designating beneficiaries for your accounts and insurance policies.
- Peace of mind: Effective financial planning provides peace of mind by ensuring that you are prepared for life’s uncertainties and have a clear path to achieve your financial goals. This reduces stress and allows you to focus on other aspects of your life.
In conclusion, effective financial planning is essential for achieving your financial goals, managing your finances efficiently, and securing your financial future. By regularly reviewing and adjusting your financial plan, you can adapt to changes in your personal circumstances and the economic environment, ensuring long-term financial success.

Fundamentals of financial planning
Financial planning involves the process of setting goals, evaluating one’s current financial situation, and creating a roadmap to achieve those goals. It encompasses various aspects of personal finance and aims to ensure that individuals or households can effectively manage their money, build wealth, and secure their financial future. Here are some fundamental principles of financial planning:
- Goal Setting
- Budgeting
- Emergency Fund
- Debt Management
- Investment Planning
- Retirement Planning
- Insurance Planning
- Tax Planning
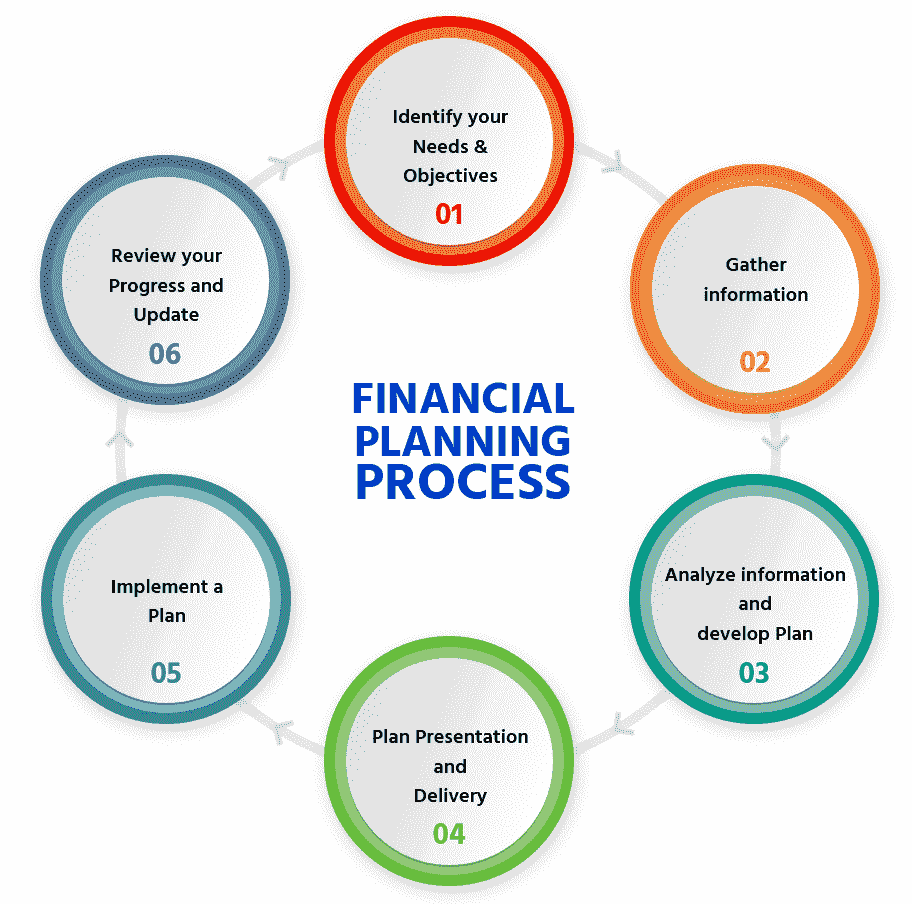
Key Components of Financial Planning / Types of Financial Planning / 6 areas of financial planning
A comprehensive financial plan comprises several key components that work together to form a cohesive strategy for achieving financial goals. Let’s explore these components in detail:
Setting financial goals
The first step in financial planning is to identify and prioritize financial goals. Whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a house, paying off debt, or funding a child’s education, setting clear goals helps in defining the path and allocating resources accordingly.
Budgeting and expense management
Creating a budget is crucial for effective financial planning. A budget allows individuals to track their income, expenses, and savings, ensuring that they spend within their means. By monitoring and controlling expenses, individuals can allocate funds towards their goals and avoid unnecessary debt.
Saving and investing
Saving and investing play a vital role in financial planning. Saving money allows individuals to build an emergency fund and have funds available for short-term goals. Investing, on the other hand, helps grow wealth over the long term by generating returns on the invested capital. A well-diversified investment portfolio tailored to an individual’s risk tolerance and financial goals can provide financial security and growth.
Risk management and insurance
Managing financial risks is an integral part of financial planning. Individuals should assess their insurance needs, such as health insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, and property insurance, to protect against unforeseen events that may have significant financial implications.
Tax planning
Tax planning involves understanding the tax implications of various financial decisions and optimizing one’s tax liabilities. By utilizing tax-efficient investment strategies, deductions, and credits, individuals can minimize their tax burdens and maximize their savings.
Estate planning
Estate planning involves preparing for the transfer of assets and wealth to the next generation. It includes creating a will, establishing trusts, designating beneficiaries, and considering strategies to minimize estate taxes. Proper estate planning ensures that individuals’ assets are distributed according to their wishes and can help mitigate potential conflicts among heirs.
By incorporating these key components into a financial plan, individuals can create a roadmap that aligns with their goals and maximizes their financial well-being.
Steps to Create a Financial Plan

Creating a financial plan involves a series of steps that help individuals assess their current financial situation, set goals, and develop strategies to achieve those goals. Let’s outline these steps:
Assessing current financial situation
To create an effective financial plan, it’s important to evaluate the current financial standing. This includes assessing income, expenses, debts, assets, and liabilities. Understanding the financial landscape provides a foundation for setting realistic goals and determining the resources available for achieving them.
Setting short-term and long-term goals
Based on personal aspirations and financial priorities, individuals should establish short-term and long-term goals. Short-term goals may include saving for a vacation or paying off credit card debt, while long-term goals can involve retirement planning, purchasing a home, or funding children’s education. Setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals ensures clarity and facilitates effective planning.
Creating a budget and tracking expenses
Developing a budget is a fundamental aspect of financial planning. It involves categorizing income and expenses, allocating funds to various categories, and tracking spending patterns. By adhering to a budget, individuals can control their expenses, identify areas for cost reduction, and allocate surplus funds towards savings and investments.
Establishing an emergency fund
An emergency fund is a crucial component of financial planning. It acts as a safety net during unexpected events such as job loss, medical emergencies, or major repairs. Aim to save three to six months’ worth of living expenses in an easily accessible account to ensure financial stability during challenging times.
Developing an investment strategy
Investing wisely is essential for long-term financial growth. Individuals should assess their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon to create an investment strategy that aligns with their financial plan. Diversification, asset allocation, and regular portfolio reviews are key considerations for successful investing.
Evaluating insurance needs
Insurance is a critical component of risk management. Conducting a thorough analysis of insurance needs ensures adequate coverage for life, health, disability, property, and liability. It’s important to review policies regularly and make necessary adjustments to accommodate changing circumstances.
Considering tax implications
Tax planning is an integral part of financial planning. Individuals should stay informed about relevant tax laws and regulations to optimize their tax liabilities. Utilizing available deductions, credits, and tax-efficient investment vehicles can minimize the tax burden and maximize savings.
Planning for retirement
Retirement planning is a major financial goal for many individuals. Assessing retirement needs, estimating retirement expenses, and creating a strategy to accumulate sufficient funds are essential steps. Retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or individual retirement accounts (IRAs), offer tax advantages and should be utilized effectively.
Reviewing and adjusting the plan regularly
Financial planning is not a one-time activity but a continuous process. Regularly reviewing the financial plan, tracking progress, and making necessary adjustments is crucial. Life circumstances, financial markets, and personal goals may change over time, necessitating modifications to the plan to ensure its effectiveness.
By following these steps, individuals can create a personalized financial plan that provides a roadmap for achieving their financial objectives.

Tips for Successful Financial Planning / How to Make a Financial Plan.
Successful financial planning requires discipline, commitment, and informed decision-making. Here are some tips to enhance your financial planning journey:
Start early and be consistent
Time is a powerful ally in financial planning. The earlier you start planning and implementing your strategies, the greater the potential for long-term financial growth. Consistency in saving, investing, and sticking to your financial plan is key to achieving your goals.
Seek professional advice if needed
Financial planning can be complex, and seeking professional advice from a qualified financial advisor may be beneficial. An experienced advisor can provide personalized guidance, help navigate complex financial matters, and ensure your plan aligns with your objectives and risk tolerance.
Educate yourself about personal finance
Empower yourself with knowledge about personal finance. Read books, attend seminars, follow reputable financial websites, and stay informed about market trends. Understanding concepts such as investing, budgeting, debt management, and tax planning enables informed decision-making and enhances your financial literacy.
Track your progress regularly
Regularly monitoring your financial progress is essential. Review your budget, track expenses, and assess how you are progressing towards your goals. This evaluation allows you to make necessary adjustments, identify areas for improvement, and celebrate milestones along the way.
Be disciplined and make necessary adjustments
Financial planning requires discipline and adherence to your financial goals. Avoid impulsive spending, unnecessary debt, or deviating from your budget. Be mindful of your financial decisions and make adjustments when circumstances change or new opportunities arise.
Stay updated with financial news and trends
Keep abreast of financial news, economic trends, and changes in the regulatory landscape. Staying informed about market conditions, interest rates, tax laws, and investment opportunities helps you make informed decisions and adapt your financial plan accordingly.
By incorporating these tips into your financial planning approach, you can enhance your chances of achieving financial stability and success.

Common Financial Planning Mistakes to Avoid
While embarking on your financial planning journey, it’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls and avoid them. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
Neglecting emergency funds
Failing to prioritize an emergency fund can leave you vulnerable to unexpected financial shocks. Without sufficient savings, individuals may resort to high-cost borrowing or deplete their long-term investments. Aim to build an emergency fund to cover at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses.
Overspending and living beyond means
Excessive spending, accumulating debt, and living beyond your means can derail your financial plan. It’s important to differentiate between needs and wants, practice mindful spending, and resist the temptation of impulsive purchases. Stick to your budget and prioritize saving and investing.
Failing to diversify investments
Over-reliance on a single investment or asset class exposes individuals to unnecessary risk. Diversification is crucial to reduce the impact of market volatility. Allocate your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to mitigate risk and enhance potential returns.
Ignoring insurance coverage
Inadequate insurance coverage can have severe financial consequences. Failing to protect against risks such as health issues, accidents, property damage, or liability can result in significant financial losses. Evaluate your insurance needs regularly and ensure adequate coverage for various aspects of your life.
Not having a retirement plan
Delaying retirement planning or underestimating the required funds can lead to financial insecurity in your golden years. Start saving for retirement early, take advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans, and consider consulting a financial advisor to estimate the amount you’ll need to maintain your desired lifestyle.
Neglecting tax planning
Tax planning is an integral part of financial planning. Failing to optimize your tax liabilities can result in missed opportunities to save money. Stay updated on tax laws, utilize available deductions and credits, and consider tax-efficient investment strategies.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can strengthen your financial plan and increase the likelihood of achieving your financial goals.

The Role of Financial Advisors
Working with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance and expertise in navigating the complexities of financial planning. Here’s how a financial advisor can assist you:
Benefits of working with a financial advisor
- Expertise: Financial advisors possess specialized knowledge and experience in personal finance, investments, tax planning, and risk management. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations tailored to your unique circumstances.
- Objective perspective: Financial advisors provide an unbiased viewpoint on your financial situation. They can identify blind spots, uncover opportunities, and offer objective advice.
- Holistic approach: A financial advisor takes into account all aspects of your financial life, including income, expenses, investments, taxes, insurance, and retirement planning. They help integrate these elements into a comprehensive financial plan.
- Accountability and motivation: Having a financial advisor can provide accountability, keeping you on track with your goals and encouraging you to make necessary adjustments. They act as a trusted partner throughout your financial journey.
How to choose a reliable financial advisor
When selecting a financial advisor, consider the following factors:
- Qualifications: Look for advisors with relevant qualifications, such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designations. These certifications indicate a certain level of expertise and professionalism.
- Experience: Evaluate the advisor’s experience and track record. Consider their years in the industry, client testimonials, and areas of specialization.
- Fiduciary duty: Choose an advisor who adheres to a fiduciary standard, which means they are legally obligated to act in your best interests.
- Fee structure: Understand the advisor’s fee structure and ensure it aligns with your preferences. Advisors may charge a percentage of assets under management, hourly fees, or fixed fees.
- Compatibility: Establish a rapport with your advisor. Open communication, trust, and shared values are important for a successful advisor-client relationship.
Collaborating with a financial advisor can provide peace of mind, guidance, and a professional partner to help you achieve your financial goals.

Why it is important to plan one’s own finances?
Planning one’s own finances is important for several reasons:
- Achieving financial goals
- Managing cash flow
- Minimizing debt
- Maximizing savings and investments
- Optimizing tax situation
- Preparing for retirement
- Managing risk
How Much Money required for Financial Planning?
Your unique financial condition and goals will determine how much money you need for financial planning. Anyone who wishes to achieve financial stability and security should engage in financial planning, not just the wealthy.
Even though you may not have much money to invest when you first start out, it is still crucial to make a budget, control your cash flow, and begin saving. You can work with a financial planner to create a more thorough financial plan that incorporates investing strategies, retirement planning, and risk management as your income and assets increase.
It is crucial to remember that financial planning is a continuous process that calls for continuing assessment and adjustment. Your financial plan may need to be revised as your financial situation and the economy change in order to stay current and useful.
In conclusion, your unique financial condition and aspirations will determine how much money you need for financial planning. Financial planning is a crucial tool for achieving long-term financial stability and security, regardless of your income or assets.
What are the 5 steps of financial planning?
- Establishing goals and objectives: The first step in financial planning is to establish your financial goals and objectives. This includes short-term goals, such as paying off debt or saving for a vacation, as well as long-term goals, such as buying a home or planning for retirement.
- Gathering data and analyzing your financial situation: The second step is to gather data about your current financial situation, including your income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flow. This information is then analyzed to identify areas for improvement and develop a plan to achieve your financial goals.
- Developing a financial plan: The third step is to develop a comprehensive financial plan that includes strategies for managing cash flow, minimizing debt, maximizing savings and investments, optimizing tax situation, preparing for retirement, and managing risk. This plan should be tailored to your individual financial situation and goals.
- Implementing the plan: The fourth step is to implement the financial plan by taking action on the strategies outlined in the plan. This may include opening investment accounts, setting up automatic savings, negotiating lower interest rates on debt, and obtaining appropriate insurance coverage.
- Monitoring and reviewing the plan: The final step is to monitor and review the financial plan on a regular basis to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This includes tracking your progress towards your financial goals, adjusting the plan as needed to reflect changes in your personal circumstances and the economic environment, and seeking professional advice when necessary.
What are the 4 basics of financial planning?
- Budgeting,
- saving,
- investing, and
- debt management
These are the four fundamental components of financial planning, in my experience as a financial analyst.
Making a plan for your income and expenses through budgeting helps you manage your money wisely and prevent overspending. Saving entails putting money aside for future objectives like emergencies, retirement, or a down payment on a property. In order to get a return on your investment, investing entails using your money to purchase stocks, properties, or other assets. Debt management is paying off any unpaid bills, including credit card balances and loans, as well as refraining from taking on additional debt in the future.

Financial planning case study examples
| Types of Planning: | Case Study / Example |
| 1. Retirement Planning: | A couple in their mid-50s approached a financial planner to help them plan for their retirement. The planner analyzed their current financial situation, including their income, expenses, assets, and debts. Based on this analysis, the planner recommended a retirement savings plan that would allow the couple to retire comfortably at age 65. The plan included a mix of investments, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, as well as strategies for minimizing taxes and managing risk. |
| 2. Estate Planning: | A wealthy individual approached a financial planner to help them plan their estate. The planner analysed the individual’s assets, including real estate, investments, and business interests, and recommended a plan for distributing these assets to their heirs. The plan included strategies for minimizing estate taxes, protecting assets from creditors, and ensuring that the individual’s wishes were carried out after their death. |
| 3. Education Planning: | A family with young children approached a financial planner to help them save for their children’s education. The planner recommended a 529 college savings plan, which allows families to save for education expenses tax-free. The planner also recommended a mix of investments, such as stocks and bonds, to maximize the family’s returns and minimize risk. |
| 4. Debt Management: | A young professional approached a financial planner to help them manage their debt. The planner analyzed the individual’s income, expenses, and debts, and recommended a plan for paying off their debts as quickly and efficiently as possible. The plan included strategies for consolidating high-interest debts, such as credit card balances, and prioritizing payments to minimize interest charges. |
These are just a few examples of the types of financial planning case studies that a financial analyst may encounter. Each case is unique and requires a customized approach based on the individual’s financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance.
Financial planning for business owners
Financial planning for business owners involves creating a comprehensive financial plan that takes into account the unique needs and goals of the business. As a financial analyst, I can tell you that financial planning for business owners typically involves the following steps:
- Goal Setting: The first step in financial planning for business owners is to identify the business’s financial goals and objectives. This may include increasing revenue, reducing expenses, improving profitability, and expanding the business.
- Cash Flow Management: Cash flow management is critical for business owners, as it ensures that the business has enough cash on hand to meet its obligations and invest in growth opportunities. Financial planners can help business owners develop a cash flow management plan that includes strategies for managing accounts receivable, accounts payable, and inventory.
- Tax Planning: Business owners are often subject to complex tax regulations, so tax planning is a critical component of financial planning. This may involve strategies such as tax-loss harvesting, depreciation, and tax credits.
- Retirement Planning: Business owners need to plan for their own retirement, as well as the retirement of their employees. Financial planners can help business owners develop a retirement plan that includes strategies such as 401(k) plans, profit-sharing plans, and pension plans.
- Risk Management: Business owners are exposed to a variety of risks, including market risk, credit risk, and liability risk. Financial planners may recommend strategies such as insurance, asset protection, and risk mitigation to manage these risks.
- Succession Planning: Business owners need to plan for the transfer of their business to future generations or new owners. This may involve developing a succession plan, creating a buy-sell agreement, and establishing a family office.
- Investment Planning: Business owners may have excess cash that they want to invest in order to grow their wealth. Financial planners can help business owners develop an investment plan that includes strategies such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments
Overall, financial planning for business owners requires a customized approach that takes into account the unique needs and goals of the business. By working with a skilled financial planner, business owners can achieve their financial objectives and grow their business over the long term.
Financial planning questionnaire
As a financial analyst, we can provide you with a list of questions that are typically included in a financial planning questionnaire. These questions gather information about your financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance, which can then be used to develop a personalized financial plan. Please keep in mind that this is just a starting point, and a professional financial planner may ask additional questions based on your specific circumstances.
- Personal Information:
- Name
- Date of birth
- Marital status
- Number of dependents
- Contact information
- Employment and Income:
- Current occupation
- Annual income
- Expected annual salary growth
- Other sources of income (e.g., rental income, dividends, etc.)
- Financial Goals:
- Short-term goals (1-3 years)
- Medium-term goals (4-10 years)
- Long-term goals (10+ years)
- Retirement age and desired retirement lifestyle
- Current Assets:
- Cash and cash equivalents (e.g., checking and savings accounts)
- Investments (e.g., stocks, bonds, mutual funds, etc.)
- Real estate
- Retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k), IRA, etc.)
- Other assets (e.g., business interests, collectibles, etc.)
- Current Liabilities:
- Mortgage(s)
- Student loans
- Credit card debt
- Personal loans
- Other outstanding debts
- Insurance Coverage:
- Life insurance
- Disability insurance
- Health insurance
- Property and casualty insurance
- Long-term care insurance
- Risk Tolerance:
- How would you describe your risk tolerance (e.g., conservative, moderate, aggressive)?
- How would you react to a significant market downturn?
- What is your investment time horizon?
- Estate Planning:
- Do you have a will or trust in place?
- Have you designated beneficiaries for your assets?
- Do you have a power of attorney and healthcare directive?
Once you have gathered this information, a financial planner can use it to develop a comprehensive financial plan tailored to your specific needs and goals. Remember that financial planning is an ongoing process, and it’s essential to review and update your plan regularly to ensure it remains aligned with your changing circumstances and objectives.
Conclusion
Financial planning is a crucial aspect of building a secure and prosperous future. It enables individuals to set clear goals, manage their finances effectively, and make informed decisions. By following the key components of financial planning, creating a personalized financial plan, and avoiding common mistakes, individuals can enhance their financial well-being.
Remember, financial planning is a dynamic process that requires regular review and adjustment. Stay disciplined, stay informed, and seek professional advice when needed. With a solid financial plan in place, you can navigate life’s uncertainties and work towards a brighter financial future.
FAQs :
How much should I save for retirement?
The amount you should save for retirement depends on various factors, including your desired lifestyle, retirement age, and expected expenses. Consulting a financial advisor can help you estimate the required funds based on your specific circumstances.
Do I need a financial advisor if I have a small income?
Financial advisors can provide value regardless of income level. They can assist in budgeting, debt management, and optimizing your financial resources to achieve your goals.
Can I create a financial plan on my own?
While it's possible to create a financial plan on your own, working with a financial advisor can provide expertise, objectivity, and holistic guidance that may enhance the effectiveness of your plan.
Is financial planning only for wealthy individuals?
Financial planning is beneficial for individuals at all income levels. It helps in managing expenses, saving for goals, and ensuring long-term financial stability, regardless of wealth.


1 Comment
Pingback: How to Scare Insurance Adjuster & Get a Fair settlement 100% Sure - Info Clubz